
FIREPROOF GRILL

FIREPROOF BANDS
Many fires spread to adjacent spaces, sometimes reaching catastrophic dimensions and causing very high losses, as the adequate protection of the openings through which pipes and other technical installations are crossed is not ensured.
This can happen because this protection is not guaranteed during the construction and rehabilitation of buildings, or because, in the exploration phase of the buildings, the existing fire resistant seals are not properly maintained or repaired.
There are several types of fire resistant gaskets. Some are specific to certain types of applications, others are more versatile, offering a wide range of options in terms of application.
For this reason, Cortartec has developed a wide range in order to meet the needs of all works and/or projects: fire cord,
The proper selection of fire-stop systems and their regular maintenance are essential to ensure that in the event of a fire, they present the expected performance and, therefore, prevent the fire from spreading to adjacent compartments.
Passive fire protection includes partitioning the entire building through the use of walls and floors classified as fire resistant. The organization into smaller fire compartments, dividing one or more rooms, or floors, prevents or delays the spread of fire from the fire source room to other spaces in the building, limiting damage to the building and providing more time for building occupants to an emergency evacuation or to reach an area of refuge.
Passive fire protection measures are intended to contain the fire in the original fire compartment, thereby limiting the spread of fire and smoke for a limited period of time as determined by the local building code and fire code. Passive fire protection measures, such as fire joints, fire walls and technical fire breaks, are tested to determine the fire resistance rating of the final assembly, usually expressed in terms of hours of fire resistance .
Unlike active fire protection measures, passive fire protection measures typically do not require electrical or electronic activation or a certain degree of movement. The exceptions to this particular rule of thumb are fire dampers (fire resistant grilles inside the air ducts) and fire door closers, which must have movement to open and close to function, as well as all intumescent products, which they swell, so they move, to function.
As the name suggests, passive fire protection remains inactive in the cladding system until a fire occurs. There are basically two types of PPCI: intumescent fire protection and vermiculite fire protection. In fire protection with vermiculite, the structural steel members are covered with vermiculite materials, mainly a very thick layer. This is a cheaper option compared to an intumescent one, but it is very crude and aesthetically unappealing. Furthermore, if the environment is corrosive by nature, the vermiculite option is not advisable, as there is a possibility of water infiltration (due to the porous nature of the vermiculite), making it difficult to check for corrosion. Intumescent fireproof is a coat of paint that is applied together with the coating system on structural steel elements. The thickness of this intumescent coating depends on the steel section used. For DFT (dry film thickness) calculation, a factor called Hp / A (heated perimeter divided by cross-sectional area), referred to as “section factor” and expressed in m -1 , is used. Intumescent coatings are applied as an intermediate layer in a coating system (primer, intermediate and finish/finish). Due to the relatively low thickness of this intumescent coating (usually in the 350 to 700 micron range), good finish and anti-corrosive nature, intumescent coatings are preferred on the basis of aesthetics and performance.
In the event of a fire, the steel structure will eventually collapse when the steel reaches its critical core temperature (about 550 degrees Celsius or 850 degrees Fahrenheit). The PCF system will only delay this point by creating a layer of charcoal between the steel and the fire. Depending on the requirement, PCF systems can provide fire ratings in excess of 120 minutes. PCF systems are highly recommended in infrastructure projects as they can save lives and property.
A building’s PCF system can be described as a group of systems within a plan. A fire joint, for example, is a system based on a product certification list. It forms part of a wall or floor classified as fire resistant, and that wall or floor forms part of a fire compartment that is an integral part of the overall fire safety plan for the building. The building itself, as a whole, can also be seen as a system.
Intumescent Cushions: consist of granules enclosed in fire-retardant fabric bags, recommended for application in places where crossings are not completed or are temporary. They are available in various shapes and dimensions. As they are removable, they are especially suitable for locations where technical installations are frequently changed.
Intumescent Collars: They consist of a steel body filled with an intumescent material that expands in contact with the fire until the strangulation of the tube where it is applied. If there is a risk of fire on both sides of the crossing, then the pipe must be protected by intumescent collars on both sides of the crossing or passage.
Intumescent Sleeves: They are made of an intumescent material that, in contact with fire, expands to the strangulation of the tube where they are installed. Contrary to what happens with collars, the intumescent material of the intumescent sleeves is not protected by an external structure, which is why it is recommended that this type of seal be installed inside the crossing. They are recommended for crossings made with piping made of flammable materials.
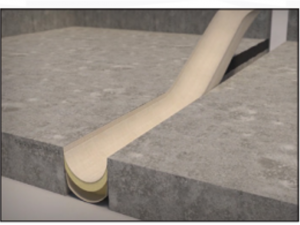
Fire break joints: They are made of materials such as ceramic fiber or others, and are suitable for application in vertical and horizontal joints where high ranges of motion are foreseeable. They are particularly suitable for building expansion joints, which allow the building elements to move and absorb natural or seismic multidirectional movements.
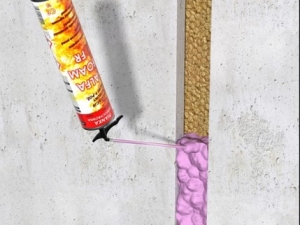
Composite CF system seals: These consist of mineral wool panels, interconnected with bitumen and coated on both sides with intumescent resin or fire-retardant thermoplastic resin, and their application is recommended for technical crossings of walls and slabs.
Modular Fire-Resisting Systems: These are special prefabricated systems based on modules designed according to the size of the ducts and the types and diameters of the cabling, which are normally installed under pressure. They are especially suitable for cables and pipes of different diameters that traverse walls and slabs in buildings and metal constructions.











 Certificado para comercialização, instalação ou manutenção de equipamentos e sistemas SCIE Nº3325
Certificado para comercialização, instalação ou manutenção de equipamentos e sistemas SCIE Nº3325  Certificado de Empreiteiro de obras públicas Nº137213
Certificado de Empreiteiro de obras públicas Nº137213